The dynamics in the consumer GPU market are slowly but surely changing. Just a few months back I would be quite hesitant to recommend AMD graphics card to those of you who are just starting out with local AI including local LLMs. Now, many of the highly popular projects such as Ollama, LM Studio and OobaBooga WebUI are getting AMD GPU compatible versions and so, here is my new top list of the best cards you can get as of now, including some more budget friendly options. Let’s begin.
This web portal is reader-supported, and is a part of the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program and the eBay Partner Network. When you buy using links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission!
How Much VRAM Do You Need?
When setting up a local system for AI tasks, one factor should be the most important to you: the amount of video memory on your GPU. For smooth and efficient LLM inference, having enough VRAM is essential. In an ideal situation, the loaded model should fit entirely within the GPU’s memory to avoid unwanted slowdowns caused by data being offloaded to system RAM. This is especially important for larger models, where high-quality results demand more operational memory.
With that said, how much do you need? At this point, the maximum amount of VRAM you’ll find on a single consumer-grade GPU is 24-32GB, which is what you should be going for if you’re serious about running larger, more complex models locally.
For smaller models, 16GB is generally considered the minimum recommended amount. 8GB of VRAM isn’t really viable anymore if you’re buying a new graphics card specifically for utilizing local LLMs.
Should You Really Pick an AMD GPU?
While NVIDIA’s CUDA platform has generally dominated the AI space, the landscape is changing rapidly. AMD has made significant progress with its ROCm (Radeon Open Compute) software stack, and the question is no longer if you can use an AMD card for AI, but rather how much value it offers. For local LLM setups on a budget, the answer is: a lot.
The primary advantage of choosing AMD is the price-to-VRAM ratio. You can often get much more memory for your money compared to an equivalent NVIDIA card, which is the single most important factor for running larger and more capable language models.
In the past, using AMD GPUs oftentimes required complex workarounds. Today, the most popular and widely used software for local LLMs, including Ollama, LM Studio, KoboldCpp, and the OobaBooga WebUI, offer out-of-the-box support for AMD graphics cards.
While NVIDIA’s CUDA ecosystem still has much wider support in some applications, for the vast majority of local AI enthusiasts, and especially for budget-conscious beginners, AMD is now a powerful and easy-to-use option that can grant you overall very good performance and value.
Best AMD GPUs For Local LLMs and AI Software – The List
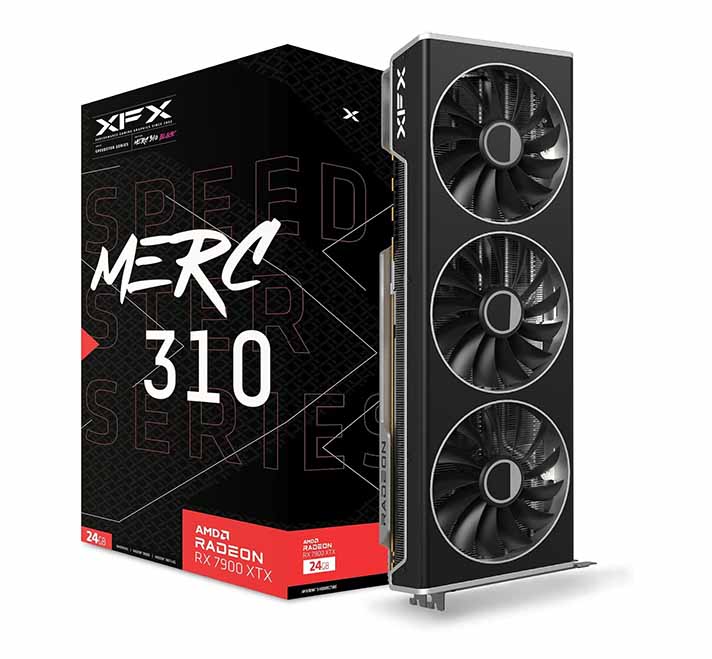
1. AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX 24GB
If you’re serious about running high-end AI models locally using AMD hardware and you have the money to spare, the Radeon RX 7900 XTX definitely is the best card on this list.
With 24GB of GDDR6 VRAM, it’s directly comparable to the NVIDIA RTX 4080 and 4090 being capable of loading many of the larger models without without needing to offload data to your system memory. This card is ideal for running more complex LLMs with higher precision, which as you might already know, should be your end goal.
NVIDIA Equivalent: GeForce RTX 4080 16GB / GeForce RTX 4090 24GB.
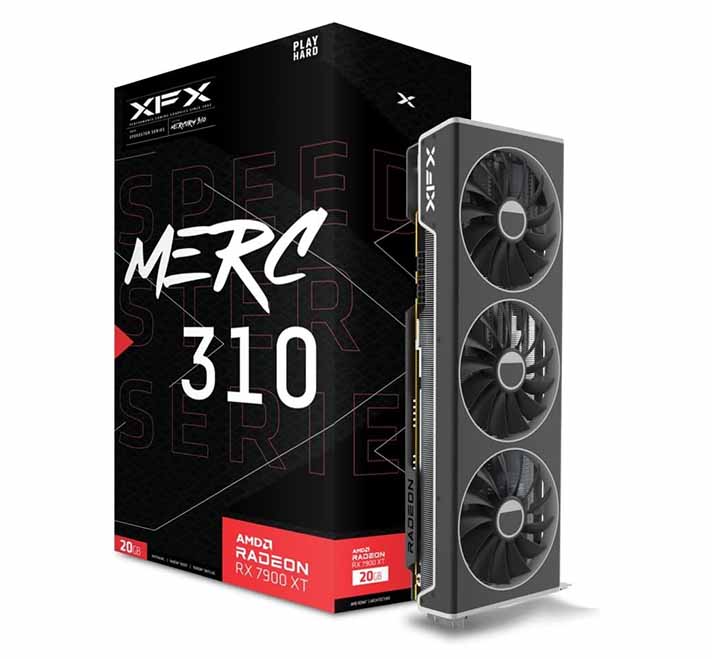
2. AMD Radeon RX 7900 XT 20GB
Just slightly below the XTX, the AMD Radeon RX 7900 XT still packs an impressive 20GB of VRAM, which is noticeably more (4GB more to be exact) than its NVIDIA equivalent – the RTX 4070 Ti.
While it’s a visible step down from 24GB of VRAM, it’s still enough to handle most larger LLMs efficiently, especially when using models with higher level of quantization. If your budget doesn’t allow for the top-tier 7900 XTX, this is also a great option for advanced AI tasks.
NVIDIA Equivalent: GeForce RTX 4070 Ti 16GB
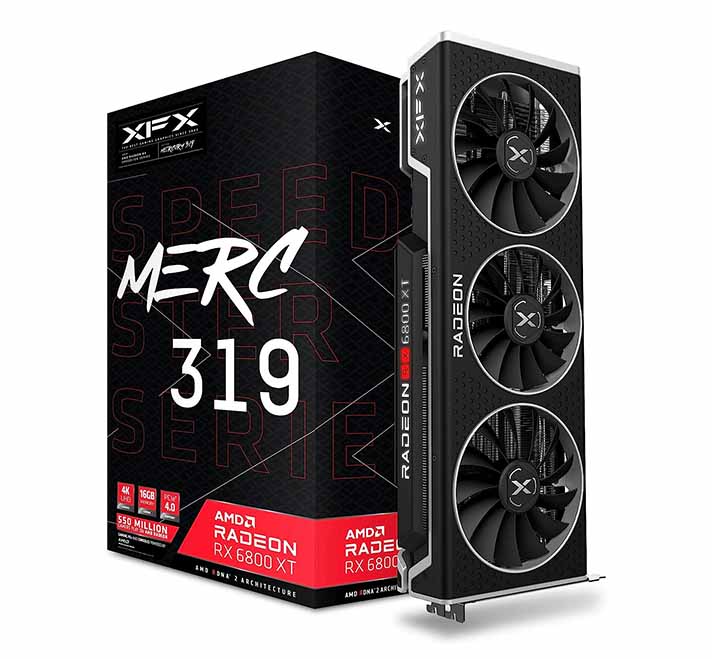
3. AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT 16GB
For users working with slightly smaller LLMs or moderate quantization levels, the AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT is an excellent middle-ground choice, coming right after the 7900 XT.
Its 16GB of VRAM is more than enough for running multiple 7B and 11B models in 4-bit quantization, and it still gives you some memory headroom when it comes to some simpler workflows. While it won’t handle the largest models with the same efficiency as the 7900 XTX, it’s still a solid performer for most local AI setups. In terms of performance, it’s closest NVIDIA counterpart seems to be the RTX 3080 10GB, or the RTX 4060 Ti 16GB.
NVIDIA Equivalent: GeForce RTX 4060 Ti 16GB
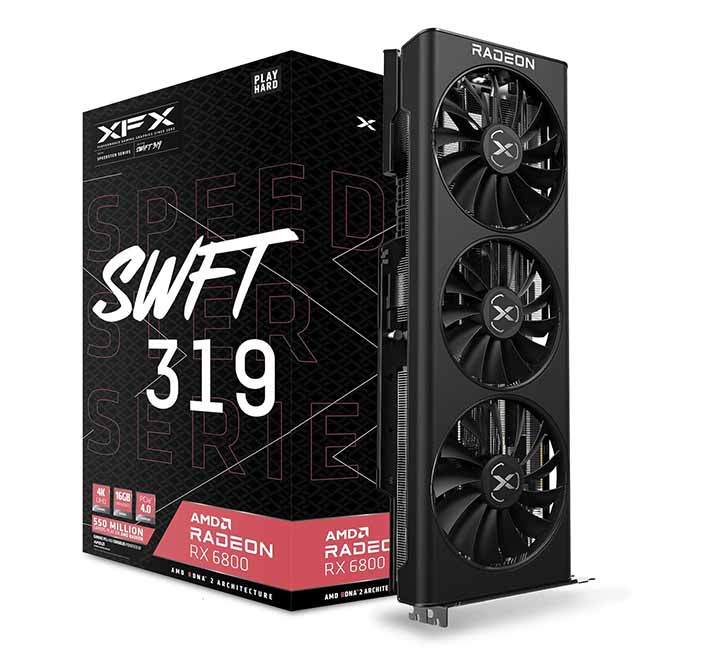
4. AMD Radeon RX 6800 16GB
There is also a non-XT variant of the previously mentioned card that’s still worth looking at. The base Radeon RX 6800, is another neat proposition from AMD.
This card also offers 16GB of VRAM, making it an event more cost-effective choice for all of you who need a solid amount of memory but don’t require top-end performance, which in most cases is a totally viable approach when talking about locally hosting smaller large language models. A pretty good choice overall, and for an even better price.
NVIDIA Equivalent: GeForce RTX 3070 8GB / GeForce RTX 3080 10GB (not really worth it with the relatively smaller amounts of VRAM they offer)
5. AMD Radeon RX 6700 XT 12GB
The AMD Radeon RX 6700 XT 12GB alongside a slightly more powerful RX 6750 XT 12GB are yet another great entry-level options, this time even more affordable.
With 12GB of VRAM, this card can still handle 7B and 11B models in 4-bit quants without any trouble. It’s the minimum recommended VRAM for some simpler local LLMs work, making it a decent choice if you’re working with basic text-editing tasks, smaller content windows, or in general, models with lower parameter counts. This is also the least expensive card on this list, without getting into the 8GB VRAM GPUs, which while they certainly can let you utilize smaller 7B models in 4-bit quantization with lower content window values, are far from being “the best” for local AI enthusiasts.
NVIDIA Equivalent: GeForce RTX 3060 12GB
6. AMD Radeon PRO W6800 32GB
This one is a little bit different. If you’re looking for an AMD card with significantly more video memory than the 7900 XTX (and the NVIDIA RTX 4090), the Radeon PRO W6800 has an astounding 32GB of GDDR6 VRAM on board, just like the NVIDIA RTX 5090.
This workstation card is quite obviously marketed more towards professional users. Its massive 32GB VRAM capacity makes it perfect for handling extremely large models and datasets, and can make fine-tuning larger models using LoRAs much easier. If your workflow involves high-precision models, heavy multitasking, or managing massive datasets, this card will deliver the memory and performance needed.
NVIDIA Competitor: NVIDIA RTX A6000 48GB (A word of warning: this one, although it does have even more video memory, is at the same time almost 4x more expensive)
You can learn much more about these types of high-VRAM cards in my article which I’ve devoted solely to them. If you’re interested, you can find it here: 12 Best High VRAM GPU Options This Year (Consumer & Enterprise)
7. AMD Radeon AI PRO R9700 32GB
For both professionals and enthusiasts lucky to have some more money to spare, AMD has recently introduced the Radeon AI PRO R9700. This workstation GPU is built on the latest RDNA 4 architecture and also comes equipped with a substantial 32GB of GDDR6 VRAM, making it an excellent choice for handling large datasets and complex models.
The Radeon AI PRO R9700 is positioned as a strong competitor to NVIDIA’s professional offerings, with a key advantage being its competitive pricing. Well, as competitive as it can get in this price range of course.
NVIDIA Competitor: NVIDIA RTX A6000 48GB
So, How To Choose? – Which One Should You Pick Up?
When it comes to local LLM inference, one rule is generally true: the more VRAM, the better. More video memory allows for faster inference by avoiding system memory offloading, which can significantly slow down your operations, especially with large models and context windows.
For those working with advanced models, 24GB VRAM cards like the RX 7900 XTX are the best bet. You could even go for the Radeon PRO W6800 or the AI PRO R9700 if you need to switch between models quickly or train LoRAs on larger models.
If you can settle for loading smaller quantized models but still require significant power, the RX 7900 XT and RX 6800 XT are solid choices.
And lastly, if you’re on a tight budget, the RX 6700 XT provides decent performance for smaller models and tasks, and can be found for even better prices if you can find a good second-hand deal.
Ultimately, your choice depends on your specific workload, the size of the models you plan to use, and your budget. While AMD may still lag behind NVIDIA in some niche AI applications, the cards above are great picks for use with compatible software.
You might also like: Best GPUs For Local LLMs (My Top Picks – Updated)








